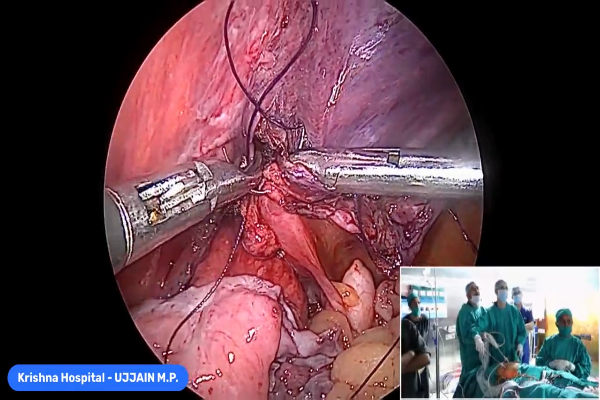
Fundoplication and TAPP
Conference Name: Laparoscopic Hernia Workshop
Conducted by: SN Krishna Hospital Ujjain Under Aegis of ASI Ujjain
Surgeon(s)/Speaker(s): Dr. Nikunj Jain & Dr. Pushpendra Jain
Surgical Procedure: Laparoscopic Hernia-Inguinal Hernias - TAPP (transabdominal preperiton...
Location: SN Krishna Hospital, Ujjain, MP
Indexsteps
1. Diagnostic Laparoscopy : Diagnostic Laparoscopy to check for Injury and prelimnary survey.
2. Identifying Anatomical Landmarks : Identifying Anatomical Landmarks: Median, Medial and Lateral Ligaments,Iliac Vessels, Vas crossing the vessel, Internal Inguinal ring, Hernial Defect.
3. Identifying Hernial Defect : Identifying Hernial Defect and noting whether it is Right or Left or both.
4. Identifying whether Hernia Is Direct or Indirect : Identifying whether Hernia Is Direct or Indirect.
5. Reducing Hernial contents : Reducing Hernial contents, if not already reduced, by gentle traction with atraumatic graspers.
6. Peritoneal Incision : Peritoneal Incision: Begin Incision 2 cms above Ant Sup Iliac Spine laterally, by picking up Peritoneum and gently incising it.
7. CO2 enters Preperitoneal Space and makes the Loose areolar tissue apparent : CO2 enters Preperitoneal Space and makes the Loose areolar tissue apparent beneath the Peritoneum.
8. The Peritoneal Incision is continued medially : The Peritoneal Incision is continued medially arching caudally so that it is 4 to 5 cms above Hernial Defects upper border.
9. Extent the Peritoneal Incision : Extent the Peritoneal Incision upto Medial Umbilical Ligament.
10. Developing Lateral Space of Bogros : Developing Lateral Space of Bogros: Continue Dissecting Peritoneum away from anterior abdominal wall and on reaching the Posterior Abdominal wall Continue dissecting off Peritoneum of it exposing the Psoas Muscle and nerves lying on it.
11. Developing Medial space of Retzius : Developing Medial space of Retzius: Continue dissecting Peritoneum off the Anterior Abdominal Wall medial to Inferior Epigastric vessels, going medial to Medial Umbilical ligament towards the midline.
12. Stay between the two Layers of Transversalis fascia : Stay between the two Layers of Transversalis fascia by being in the bloodless loose areolar tissue.
13. Dissection continues downwards towards pelvis : As the dissection continues downwards towards pelvis, Shining white Coopers Ligament comes into view.
14. Further dissection : Further dissection is done by dissecting Bladder downwards exposing the cave of Retzius.
15. Dissection of the Direct Sac : Dissection of the Direct Sac: this sac will commonly limit medial dissection and hence Sac will have to be dissected early in Medial Dissection.
16. The Sac is gently pulled off the anterior abdominal wall and Chord Structures : The Sac is gently pulled off the anterior abdominal wall and Chord Structures: they will lie lateral and posterior to sac. The shining white Pseudosac will be seen and the sac will have to be dissected off Pseudosac leaving it behind.
17. The sac will now have to be dissected off the Chord structures completely : The sac will now have to be dissected off the Chord structures completely, and off the post abdominal wall till Vas is visible, and going proximally till the Vas turns medially.
18. The Indirect sac : The Indirect sac: this will lie Lateral to the chord structures and anterior. The sac is picked up and diisected all around peeling fine layers of Fascia: as the sac is dissected and pulled medially, the chord structures come into view kying lateral and posterior to it; the sac is gently dissected off chor structures trying to develop a gap between the sac and the chord.
19. The sac will have to be cleared off medially : At this stage the sac will have to be cleared off medially and then all around leaving chord structures on the abdominal wall.
20. Once the window between sac and chord structures is seen it is further enlarged : Once the window between sac and chord structures is seen it is further enlarged and sac going distally into Internal Inguinal ring is pulled more and more inside.
21. When sufficient cms of sac is pulled inside the abdomen, sac is cut : When sufficient cms of sac is pulled inside the abdomen, sac is cut with scissors circumferentially, leaving distal sac in the scrotum.
22. The inner cut end of sac is ligated with an endoloop : The inner cut end of sac is ligated with an endoloop.
23. Parietalisation of chord : Parietalisation of chord: the sac is further dissected off the Chord structures till the vas is completely seen and it turns medially.
24. Now entire dissection is reviewed : Now entire dissection is reviewed: Medial dissection should go atleast 1 cm beyond the midline.
25. Preparation of MeshL : Preparation of MeshL: 15 * 15 cms of Polypropelene Mesh is taken and tailored: Minimum size should be 15* 12 cms. Lateral corner can be cut to take the curve of incision.
26. Mesh is folded or rolled like a cigar and introduced through 10 mm port : Mesh is folded or rolled like a cigar and introduced through 10 mm port directing it towards the area of dissection.
27. Mesh is now spread against the Anterior Abdominal wall : Mesh is now spread against the Anterior Abdominal wall, two thirds of it spread like this.
28. Lower one third of Mesh is Spread onto Postierior abdominal wall : Lower one third of Mesh is Spread onto Postierior abdominal wall tucking medial end int supravesicular retropubic space, and lateral corner tuck beneath peritoneum on the Iliopsoas.
29. Fixation of Mesh : Fixation of Mesh: The mesh is fixed medially at two places: Just above symphysis, and on the Coopers Ligament. Futher fixation is done one at upper edge of mesh medially at midline, and on laterally, above anterior superior iliac spine.
30. Fixation : Fixation can be done with nonabsorbable sutures, or fixation devices.
31. Closure of Peritoneal Flap : Closure of Peritoneal Flap: The peritoneal flap is lifted up and sutured to upper edge of Peritoneum with 2/0 absorbable or similar suture.
32. Insflation is closed and ports withdrawn and closed : Insflation is closed and ports withdrawn and closed.
port positions
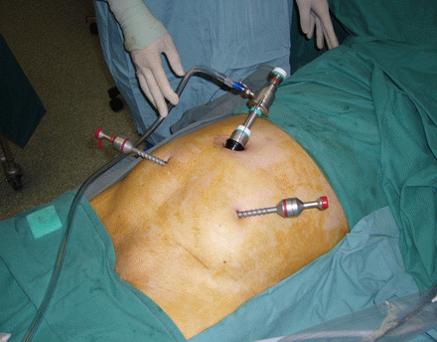
1. Port positions for Laparoscopic Hernia : Working Ports: Two. 5 mm ports on either side lateral to Rectus Sheath, in line with, or 15 degrees lower than, Umbilical Port.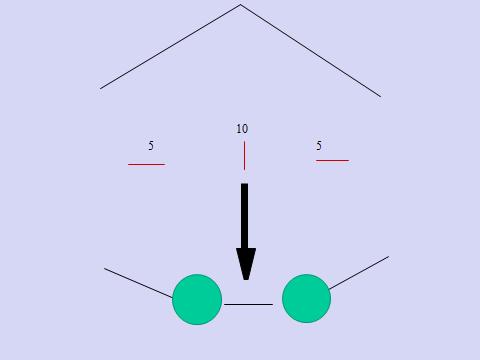
2. Port positions for Laparoscopic Hernia : Camera Port: Supra-umbilical 10mm trocar (camera port, inserted with closed technique using a Veress needle + sharp trocar or by open method)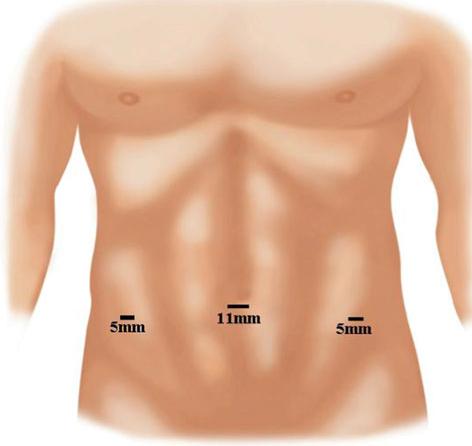
3. Working Ports : Two 5 mm ports on either side lateral to Rectus Sheath, in line with, or 15 degrees lower than, Umbilical Port.
precautionary_measures
1. First trocar : Blind entry of Veress needle and first trocar. Palmer’s point is safe entry.
2. Peritoneal incision : Peritoneal incision should not be extended medial to medial umbilical ligament as this might result in increased incidence of urinary bladder injury or bleeding from the perivesical plexus of vessels.
3. Sharp dissection in the pseudo sac : Sharp dissection in the pseudo sac area in an attempt to resect the pseudo sac may result in bleeding
4. Bladder should be drained continuously : Bladder should be drained continuously by an indwelling catheter to prevent accidental injury.
5. Separation of the sac from the cord structures : During separation of the sac from the cord structures, injury to the inferior epigastric vessels can be prevented if dissection is not continued medially beyond the level of the transversalis sling.
6. Injury to cord structures : Injury to cord structures can be prevented if the separation of the sac is performed on the upper half of the internal inguinal ring as cord structures are usually present on the inferior aspect.
7. Minimal use of monopolar or bipolar cautery : Monopolar or bipolar cautery should be used minimally as it poses a risk of injury to nerves end Vas deferens.
pre_post_measures
1. Preoperative investigations : Complete blood count:new: Blood sugar – random (fasting and postprandial, if diabetic):new: Serum creatinine:new: Liver function tests:new: Coagulation profile:new: HIV / HbsAg / Anti-HCV (if mandated by hospital):new: Blood group:new: Chest x-ray:new: ECG:new: Echocardiogram (if over 50 years):new: Abdominal ultrasound examination:new:
2. Preoperative measures : Patient is catheterized to empty the Bladder.:new: Attachment of the diathermy plate:new: Securing the patient to the table:new: Padding of the pressure points:new: Dose of prophylactic antibiotic at the time of induction of anaesthesia:new: Anti-embolic stockings / placement of an intermittent compression device on the legs:new:
3. Postoperative measures : NBM for 6 hours:new: Ambulate after that:new: Two dose of Antibiotics:new: Analgesics as required:new:
4. Warning signs in the postoperative period : Careful closure of the fascia at the umbilical trocar site:new: Infiltration of all trocar sites with local anesthetic:new: Closure of wounds and application of dressing:new: Pressure dressing is given on the Inguinal area to reduce Seroma.:new:
Surgical Instruments
1. Blunt graspers
2. 0 and 30 deg telescope
3. Fibrin glue applicator system
4. Suction irrigator / suction cannula
5. Foley catheter
6. Blunt Dissector
7. integrated trocar-dissector balloon system
8. 5 mm Trocar
9. Polypropelene Mesh
10. Mesh